Ensuring the Safety of Chemical Substances
- Goals and Achievements of Major Initiatives
- Basic Approach
- Policies and Organization
- Managing Chemical Substances
- Creating and Deploying the CIGNAS Chemical Substance Information Management System
Complying with Laws and Regulations
01 Complying with Laws and Regulations in Japan - 02 Complying with Laws and Regulations in Other Countries and Territories
- Training and Systems
01 Initiatives in Japan - 02 Initiatives at DIC Group Companies in Other Countries and Territories
- Position on the Use of Animals in Testing
- Safe Product Transport
- Ensuring the Safety of Chemical Substances
Goals and Achievements of Major Initiatives
Expand deployment of CIGNAS at DIC Group companies in other countries and territories.
| Scope of target | Fiscal year | Goals | Achievements | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
2024 |
|
|
★★★ |
|
|
★★★ | ||
| 2025 |
|
― | ― | |
|
― | ― |
Review business flows to ensure compliance with laws and regulations in Japan and in other countries and territories.
| Scope of target | Fiscal year | Goals | Achievements | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
2024 |
|
|
★★ |
|
|
★★ | ||
|
|
★★ | ||
| 2025 |
|
― | ― | |
|
― | ― | ||
|
― | ― |
- Evaluations are based on self-evaluations of current progress.
Key: ★★★ = Excellent; ★★ = Satisfactory; ★ = Still needs work
Basic Approach
The DIC Group continues working to assess risks over the entire life cycle of its products and to provide information to stakeholders to ensure products are handled appropriately.
Policies and Organization
In 2002, countries and territories participating in the World Summit on Sustainable Development (WSSD) in Johannesburg, South Africa, including the United States and Japan, agreed on a goal for the management of chemical substances to minimize the impact thereof on human health and the environment by 2020. In 2015, the United Nations (UN) General Assembly set the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a collection of common goals designed as a blueprint for global society. As a comprehensive chemicals manufacturer with operations around the world, the DIC Group has created uniform standards for managing chemical substances that exceed legal and regulatory standards well before the WSSD. In line with its Environment, Safety and Health Policy (established in 1992), the Group views product stewardship* as the foundation of Responsible Care and works to provide stakeholders with information on the appropriate handling of its products over their entire life cycle.
To help realize alternative offerings that exert less of an impact on the environment, the DIC Group promotes the management of chemical substance information as a way to contribute to sustainable product development. To this end, the Group has established a base to administer efforts in the People’s Republic of China (PRC) and created a department in Japan to oversee communication for the Asia–Pacific region, better positioning it to disseminate information to Group companies across Asia. Steps are also being taken to strengthen information sharing with the pertinent department of Sun Chemical Corporation, which oversees Group operations in the Americas and Europe.
- Product stewardship is a philosophy that emphasizes assessing product-specific risks and sharing findings and information on appropriate handling with stakeholders with the aim of reducing the environment, safety and health (EHS) impact of products over their entire life cycle, i.e., from the development of chemical substances through to procurement, production, transport, sale, use and disposal or recycling.
Managing Chemical Substances
In 2003, the UN Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) issued the first edition of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS).*1 Many countries have since introduced the GHS, including Japan, which in 2006 compelled use of the system in the Industrial Safety and Health Act. As part of its effort to ensure effective product stewardship, the foundation of Responsible Care, DIC was early to respond to this development, providing customers with crucial hazard-related information and encouraging them to use such information to reduce risks.
Concurrent with the enforcement of the Industrial Safety and Health Act in 2006, DIC began providing GHS-compliant safety data sheets (SDSs).*2 In 2009, the Company developed CIRIUS (Chemical Substance Information Comprehensive Management System), a proprietary system that centralizes the management of information on chemical substances in raw materials and products, as well as automatically checks various laws and regulations—including the Act on the Evaluation of Chemical Substances and Regulation of Their Manufacture, etc.—to facilitate swift responses to customers’ requests for information. In 2013, the Company began using the Wercs, an SDS creation system used globally that facilitates the translation of data into 46 languages, for products destined for overseas markets in Japan, while in 2015 it also deployed the Wercs at 23 Group companies in 11 countries and territories outside Japan. More recently, DIC has created a new comprehensive global chemical substance information management system that integrates the functions of the Wercs and CIRIUS. In fiscal year 2021, DIC replaced the Wercs and CIRIUS in Japan with the new system, dubbed CIGNAS (Chemicals Information Global Network Access System). Use of CIGNAS commenced at Group companies in Greater China in fiscal year 2023, replacing the Wercs and CIRIUS. In fiscal year 2024, DIC began promoting the migration of Group companies in the Asia–Pacific region to the new system from the Wercs. U.S.-based Sun Chemical, which oversees Group operations in the Americas and Europe, and its group companies have used Atrion International Inc.’s eponymous chemical substance information management system since 2006, enabling it to provide highly accurate information to its customers worldwide.
Recognizing the importance of specialized expertise in the manufacture, import and handling of chemical substances in accordance with applicable laws and regulations, in 2000 the DIC Group in Japan began providing related training. Since 2007, DIC has had a proprietary licensing system designed to maintain and enhance the skills of employees who have become experts in chemical substance management.
- The GHS was formally adopted by the UN in 2003 to facilitate the uniform global classification and labeling of hazard information for chemicals.
- SDSs contain information on the hazards of chemicals to ensure their safe handling.
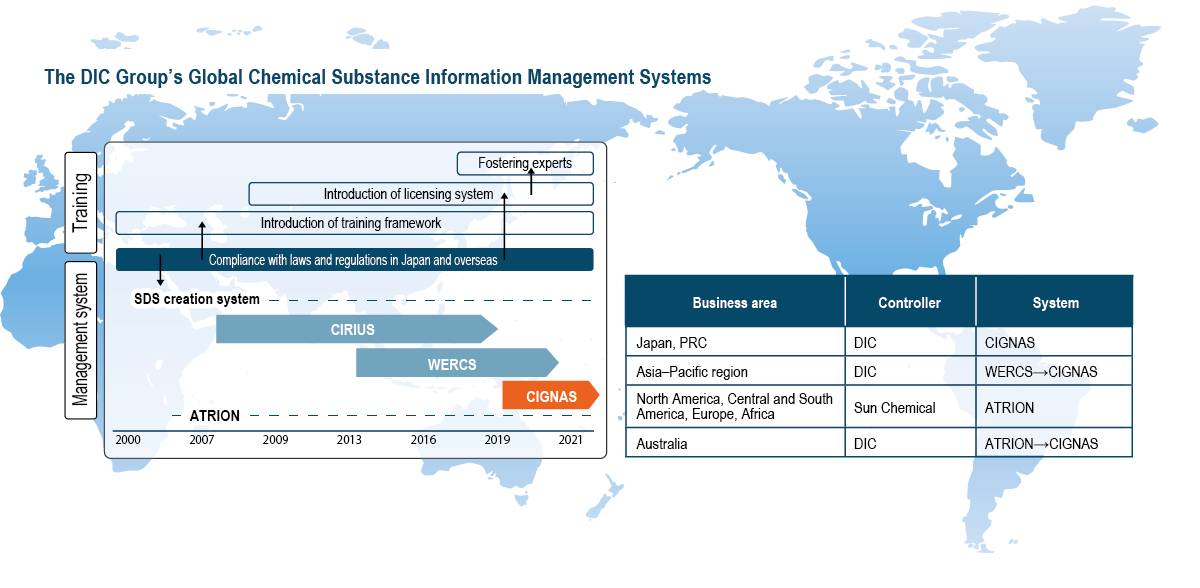
Creating and Deploying the CIGNAS Chemical Substance Information Management System
DIC applied capabilities, experience and expertise accumulated in the design, development and operation of CIRIUS and the Wercs to designing and developing the CIGNAS system with the objective of streamlining its operations. To this end, the Company set about creating a unified global framework for data integration with its enterprise resource planning (ERP) system and other internal systems.
Individual divisions and departments make use of chemical substance information in their particular work. Accordingly, the system is used not only by experts in the management of chemical substances but also by diverse other employees across the global DIC Group. The Company was thus aware of the importance of designing the interface so that even non-experts can use CIGNAS with ease to obtain the information they need. In addition, the system stores confidential information on, among others, the chemical composition of products and raw materials. For this reason, and because of the wide range of employees across Asia using the system, meticulous attention to security was a key consideration in system design and development. DIC has also established a working group to enhance CIGNAS by addressing issues that arise as the system is being deployed. This working group will continue to explore modifications to the system to improve its performance.
A Global Framework
Techniques used to manage chemical substance information vary greatly depending on country/territory and site, as does the quality of management. Given the expected further tightening of laws and regulations governing chemical substances and the increasing number and changing nature of substances used, implementing an organized global approach is essential. The DIC Group recognizes that introducing a new system is only part of the solution, and so it has also commenced efforts to establish a new information management framework to support administration of the new system after deployment. In fiscal year 2019, the Chemical Substance Information Management Group was established at DIC’s corporate headquarters in Tokyo to oversee this process. In April 2020, this group also began promoting initiatives in Greater China. In January 2023, collaboration was expanded to encompass the Asia–Pacific region. Through such efforts, the Group will leverage know-how accumulated in Japan to integrate information management, thereby guaranteeing consistent quality, securing compliance and strengthening governance.
Complying with Laws and Regulations
01Complying with Laws and Regulations in Japan
DIC recognizes legal and regulatory compliance as central to risk management. In Japan, this includes fulfilling without exception obligations related to the reporting of new chemical substances set forth in the Act on the Evaluation of Chemical Substances and Regulation of Their Manufacture, etc., and the Industrial Health and Safety Act, and to the keeping of records on manufacturing, importing and sales laid out in the Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Act. To enhance the reliability of its compliance efforts, the DIC Group is promoting diverse initiatives, from collecting and analyzing information to formulating guidelines, promoting awareness among Group companies and customers, and advancing deployment of CIGNAS. The Food Sanitation Act, which was amended in fiscal year 2018, stipulates the adoption of a Positive List system, which allows only substances that have been evaluated for safety to be used in utensils, containers and packaging for food, with a transitional period that ended in May 2025. DIC manufactures a wide range of polymers, including polystyrene, as well as inks and other raw materials, for use in food packaging and containers. Accordingly, the Company is proceeding with efforts in cooperation with pertinent industry organizations to gather information and apply to be included in the list. There were no legal violations by the DIC Group in Japan requiring the registration or reporting of chemical substances in fiscal year 2024.
Outlook for Principal Initiatives in Fiscal Year 2025
Full enforcement of Japan’s revised Industrial Safety and Health Act began in fiscal year 2023. The revised Act emphasizes the transition to a regulatory system for chemical substances based on autonomous management, notably on establishing a system for implementing autonomous management and strengthening the communication of information on hazards and toxicity. In April 2024, additions were made to the list of chemical substances that must be labeled and to items that must be noted on SDSs, while in October 2025 additions will be made to the list of chemical substances to which worker exposure must be kept below a certain concentration. The DIC Group in Japan will continue working to ensure it manages chemical substances, as well as prepares and distributes SDSs and labels, in compliance with the revised Industrial Safety and Health Act. DIC will also take decisive steps to comply with the Global Framework on Chemicals, which was discussed at the International Conference on Chemicals Management (ICCM), in 2023, paying close attention to how the new goal is reflected in policies, laws and regulations.
02Complying with Laws and Regulations in Other Countries and Territories
Recent years have brought the establishment and amendment of major laws and regulations governing chemical substances across East Asia. Key examples include revisions to the Republic of Korea (ROK)’s Act on the Registration and Evaluation of Chemicals (K-REACH) in fiscal year 2019 and the PRC’s China REACH legislation in fiscal year 2020. Other countries that currently do not have chemical substance registration systems, including Thailand, Vietnam, Turkey, and Central and South American countries, are also moving in this direction. The GHS has also been adopted and made mandatory in most countries, with latecomer India now taking steps toward enacting a law obliging GHS compliance. DIC gathers the latest information on chemical substances in overseas markets through local consultants, as well as through its global network, which includes Sun Chemical and other DIC Group companies, ensuring its ability to respond effectively to revisions to laws and regulations and to provide information to Group companies and customers.
In Japan, DIC has registered 36 substances to comply with the European Union(EU)’s REACH regulations. Individual departments collaborate to implement measures aimed at preventing shipments that violate the regulations. The Company is also taking other necessary steps, including updating its registration dossiers.
As a leading member of the Japan Chemical Industry Association (JCIA) working group charged with collecting Japanese companies’ opinions and proposals regarding the enactment and revision of laws and regulations, DIC conducts dialogue with government authorities, playing a leading role in guaranteeing the legal and regulatory compliance of JCIA members. Thanks to effective monitoring of regulatory trends and swift responses to revisions to pertinent laws, there were no violations of laws or regulations requiring the registration or reporting of chemical substances by the DIC Group in other countries and territories in fiscal year 2024.
Outlook for Principal Initiatives in Fiscal Year 2025
The DIC Group will continue pressing ahead with preparations to re-register chemical substances as required under the ROK’s revised K-REACH legislation, prioritizing substances that are close to the re-registration deadline. Additionally, the Group will continue to gather information and take steps to register chemical substances to ensure compliance with newly introduced registration systems in other countries and territories. In India, the Group will keep abreast of developments surrounding India’s mandating of GHS compliance and will submit opinions and proposals through the JCIA.
Training and Systems
01Initiatives in Japan
Fostering Experts
As a comprehensive global chemicals manufacturer, the DIC Group recognizes legal and regulatory compliance as central to risk management and promotes training designed to foster experts in this area. DIC began offering an entry-level course on laws and regulations governing chemical substances in fiscal year 2014. An online format was adopted in fiscal year 2021 to make it easier for target employees—mainly employees at sites with technical departments—to participate in training. In fiscal year 2022, the Company continued to provide training on the legal handling of chemical substances, expanding participation in this training to include employees of DIC Group companies in Japan. Beginning in fiscal year 2023, efforts focus on enhancing program content by designing pragmatic new courses that address the practical requirements of various chemicals-related laws and regulations.
Licensing Systems in Japan
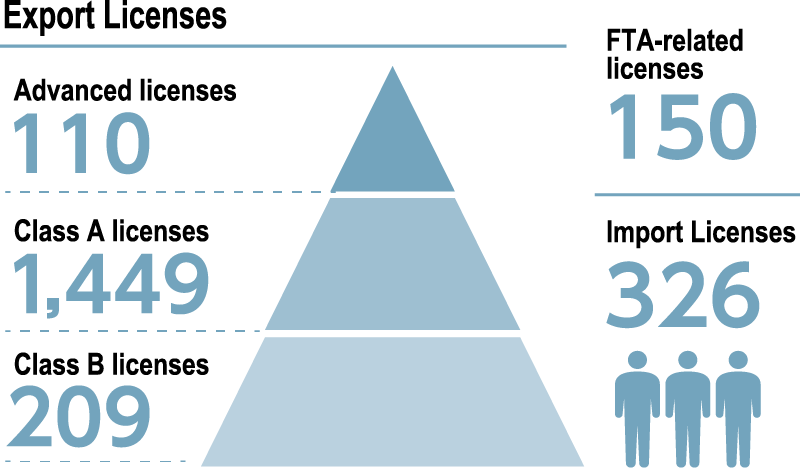
Under a proprietary licensing system, DIC provides mandatory specialized training for individuals in Japan engaged in the export and import of chemical substances and issues licenses to employees who have completed training and passed in-house examinations. The period of validity for export licenses is two years, while that for import licenses is three years. Training for individuals involved in exporting and importing chemical substances focuses on the Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Act, while that for individuals involved exclusively in importing centers on the Act on the Evaluation of Chemical Substances and Regulation of Their Manufacture, etc., the Industrial Safety and Health Act and the Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Act. To renew a license, an employee must once again go through training and pass the in-house examination. In fiscal year 2024, training and examinations were conducted online. As of the fiscal year-end, 326 employees held an import license; 209 held a Class B export license, requiring general knowledge; and 1,449 held a Class A export license, which requires high-level specialized expertise, while a further 110 had completed an advanced export license course, an achievement requiring superior capabilities. Given the increasingly challenging security export control environment, since fiscal year 2023 DIC significantly reinforced its training regarding export sanctions imposed on the Russian Federation (Class A export license training) and U.S. legal issues (advance export license training). With Japan expected to dramatically strengthen security export control for conventional weapons in fiscal year 2025, the Company will further enhance its licensing systems to include a response to this change.
In light of the increasing importance of economic partnership agreements (EPAs), owing to, among others, the entry into force of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), since fiscal year 2022 DIC has had a licensing system for employees who prepare certificates of origin based on such agreements. At present, this license is held by 150 employees. With the United Kingdom becoming a member of the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) in December 2024, this particular license has taken on even greater importance. Accordingly, the Company will continue to expand related training in fiscal year 2025.

02Initiatives at DIC Group Companies in Other Countries and Territories
Training at DIC Group Companies in Other Countries and Territories
CIGNAS was launched at 18 companies in the Asia–Pacific region in fiscal year 2024. Accordingly, the Responsible Care Department’s Chemical Substance Information Management Group spearheaded related training. This began with 17 online training sessions during the prelaunch period on how to operate CIGNAS and related systems for employees of all 18 companies. This training enabled employees to learn basic operating procedures and practice these on their own before going live. After a certain amount of time had passed, a total of 25 Q&A sessions were held to respond to questions that may have arisen over the course of training. These sessions included showing actual operating displays to clarify employees’ questions and deepen their understanding.
VOICE
DIC and Sun Chemical are strengthening collaboration through new chemical substance management initiatives.
DIC and Sun Chemical have initiated new collaborative efforts in the areas of chemical risk assessment and chemical management laws and regulations. This partnership aims to enhance support in various areas, including poorly soluble particles, in silico toxicology,* global regulatory trends and food contact materials.
In the area of chemical risk assessment, toxicologists from both companies now work together, sharing expertise and resources to tackle these complex topics. In the area of chemical management laws and regulations, our regulatory teams have also strengthened cooperation by meeting face-to-face and establishing regular information-sharing practices. We also hold quarterly stakeholder meetings and distribute a biannual regulatory newsletter to keep everyone informed about upcoming global changes and news from industry associations. Additionally, we collaborate on specific projects, such as chemical information management and reclassification communication, seeking an efficient exchange of relevant information and ensuring clarity in safety data for customers. This structured interaction ensures that both DIC and Sun Chemical stay aligned and up-to-date with regulatory requirements, ultimately fostering more efficient and effective regulatory compliance.

Sun Chemical Corporation
Dr. Heidi Stratmann
- In silico toxicology uses computer-based simulation and data analysis to predict the toxicity of chemical substances.
Position on the Use of Animals in Testing
In line with the “3Rs” of animal use in research (replacement, reduction, refinement), which are guidelines designed to ensure the more ethical use of animals in testing, the DIC Group actively promotes safety evaluation using alternative testing methods and quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) models that do not employ animals.
Safe Product Transport
The DIC Group has created Yellow Cards containing simplified SDSs. This provides critical information to transport personnel, facilitating the appropriate responses in the unlikely event of an accident to protect the environment and ensure safety. (For more information, please see “Safety in Logistics.”)
Ensuring the Safety of Chemical Substances
DIC participates in committees and working groups related to laws and regulations governing chemical substances in Japan, as well as other countries and territories, including the Japan Chemical Industry Association (JCIA), the International Council of Chemical Associations (ICCA) and the Japan Dyestuff and Industrial Chemicals Association (JDCIA). On behalf of the chemicals industry, the Company also takes part in discussions with the Japanese government as a member of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare’s Study Group on the Management of Chemical Substances in the Workplace, an advisory body overseeing revisions to the country’s Industrial Safety and Health Act. Such efforts position the Company to anticipate both domestic and international regulatory trends, including those pertaining to restrictions on manufacturing and imports, and to take steps—including formulating plans to phase out, or to limit or prohibit the use of, pertinent substances before such restrictions are imposed.
To ensure the effectiveness of these steps, the DIC Group has formulated the DIC Group Green Procurement Guidelines, which outline criteria for the raw materials it procures, and strives to eliminate hazardous substances by using only raw materials that
- do not contain hazardous substances the production of which is prohibited under Article 55 of the Industrial Safety and Health Act;
- do not contain Class I specified chemical substances designated by Japan’s Act on the Evaluation of Chemical Substances and Regulation of Their Manufacture, etc. (excluding substances the use of which is legally permitted);
- do not contain chemical substances designated for monitoring by Japan’s Act on the Evaluation of Chemical Substances and Regulation of Their Manufacture, etc. (excluding catalysts);
- do not contain specified chemical substances the production of which is already prohibited under Japan’s Act on the Protection of the Ozone Layer through the Restriction of Specified Substances, etc.;
- do not contain specified particulates designated by Japan’s Air Pollution Control Act; and
- do not contain specified poisonous and deleterious substances designated by Japan’s Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Act.

