Reducing Industrial Waste
Goals and Achievements of Major Initiatives
Reduce industrial waste disposed of as landfill (achieve zero emissions).
Reduce industrial waste generated
by production facilities.
| Scope of target | Japan |
|---|---|
| Goal for fiscal year 2022 |
|
| Achievements in fiscal year 2022 |
|
| Evaluation | ★★★ |
| Goals for fiscal year 2023 |
|
Promote recycling.
| Scope of target | Japan |
|---|---|
| Goals for fiscal year 2022 | Resource recycling rate* DIC Group (Japan): 90% |
| Achievements in fiscal year 2022 | Resource recycling rate: 91% |
| Evaluation | ★★★ |
| Goals for fiscal year 2023 | Resource recycling rate DIC Group (Japan): 80% |
- Resource recycling rate: (Volume of industrial waste recycled + Waste heat recovered) / Volume of industrial waste generated
- Evaluations are based on self-evaluations of current progress.
Key: ★★★ = Excellent; ★★ = Satisfactory; ★ = Still needs work
Policies and Organization
Basic Approach
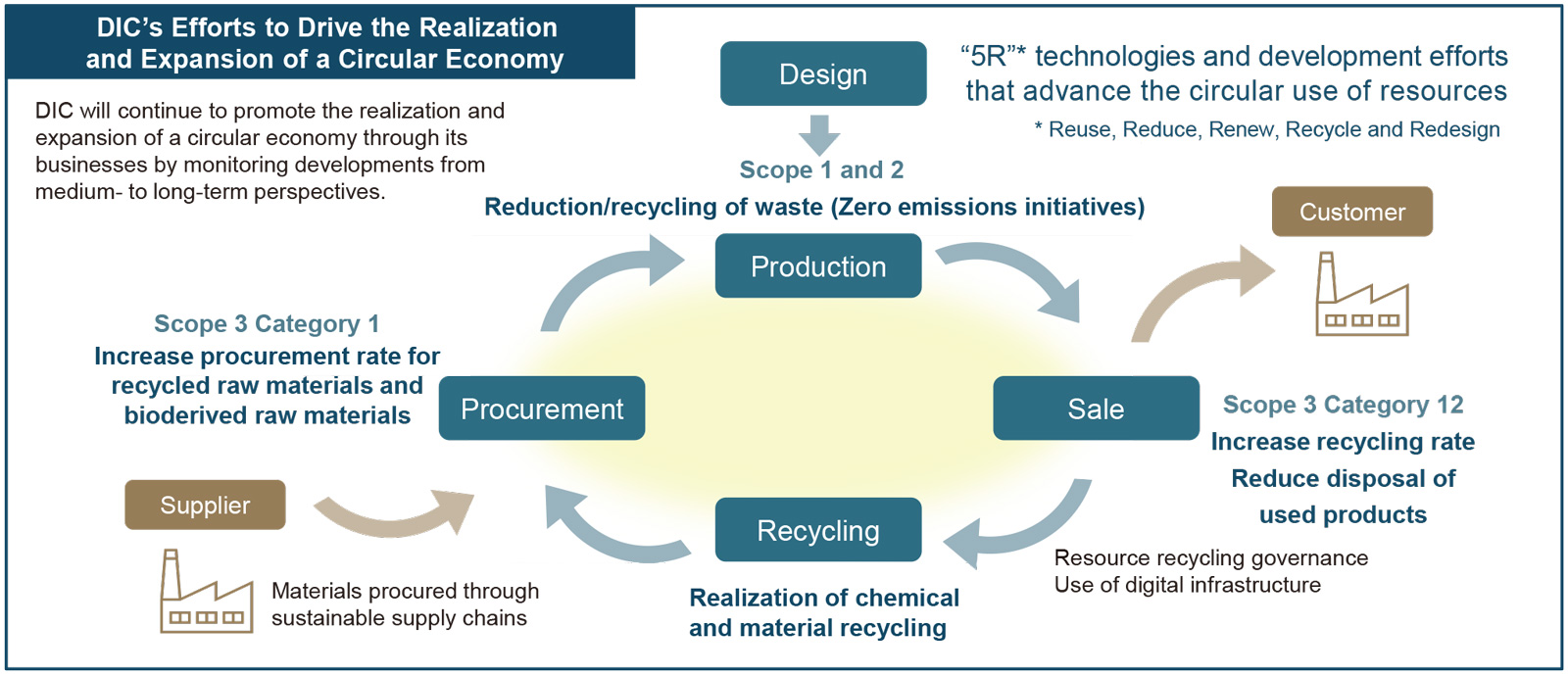
To promote the realization of a circular economy, the DIC Group strives to use resources effectively, as well as to reduce the impact of its disposal of industrial waste.
In seeking to promote the realization of a circular economy, the DIC Group is stepping up efforts to encourage the reuse, reduction and recycling of industrial waste. Of particular note, the Group is striving to minimize production losses by increasing throughput yields. The Group also works to fully grasp and effectively manage industrial waste at production facilities from generation through to discharge, intermediate treatment and final disposal as landfill, as well as to reduce its disposal of industrial waste as landfill and to boost its resource recycling rate by increasing recycling (material and chemical) and recovering waste heat from incineration. To ensure strict compliance, the Group has introduced a system for managing electronic manifests (e-manifests), thereby ensuring traceability. The Group also conducts on-site checks to ensure the practices of subcontracted waste disposal companies.
Principal Initiatives in Fiscal Year 2022
01DIC Group in Japan
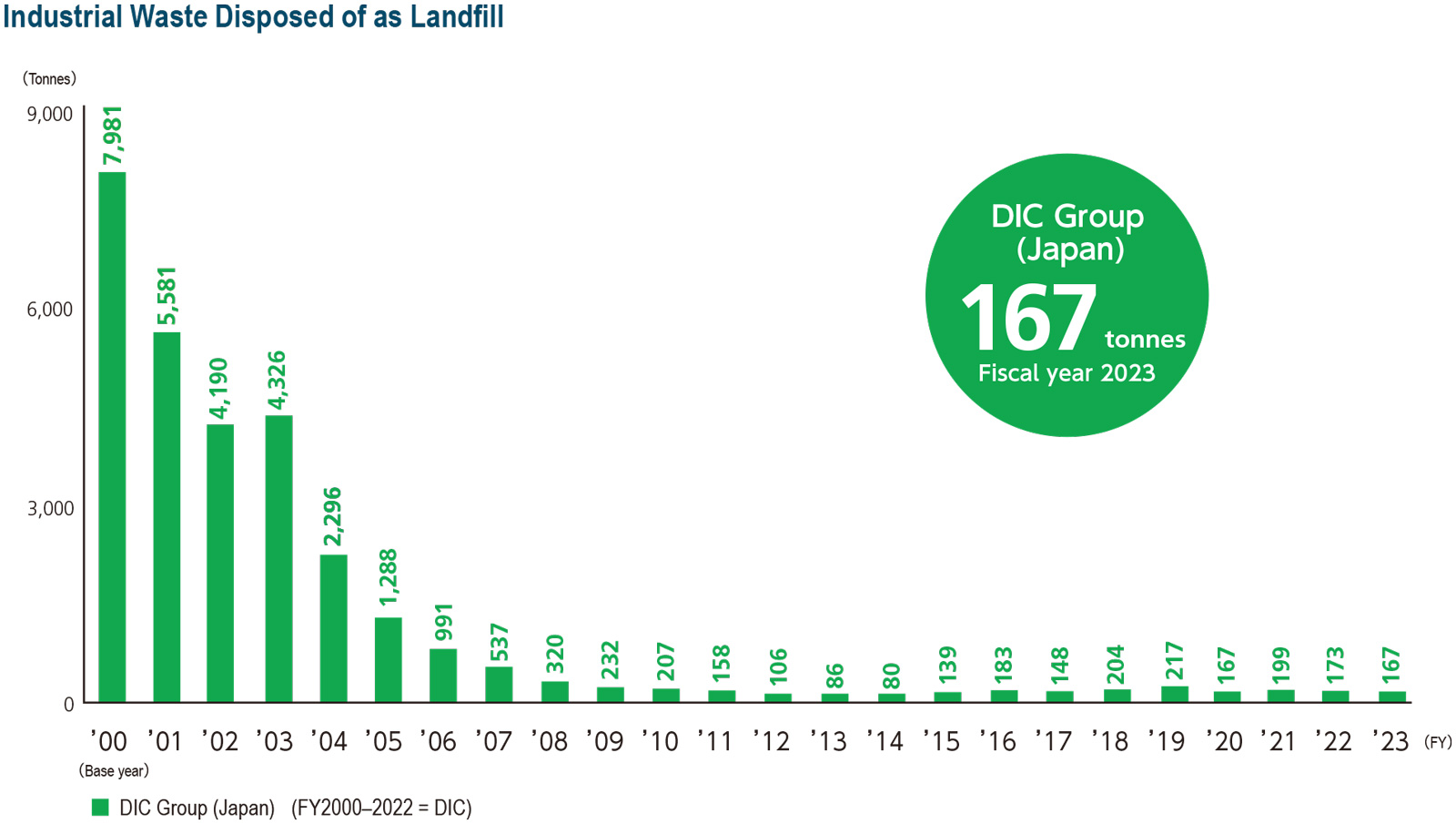
The DIC Group in Japan has long promoted zero emissions initiatives with the aim of reducing the total volume of industrial waste disposed of off-site as landfill by 95% from the fiscal year 2000 level, a target it actually achieved in fiscal year 2010. The Group is currently working to maintain the annual industrial waste it disposes of as landfill at this level (200 tonnes). With efforts to shift toward a circular economy intensifying in recent years, the Group is now also working to reduce waste generated and waste discharged by Group production facilities as well as to curb waste disposed of as landfill and has set a target for the former.
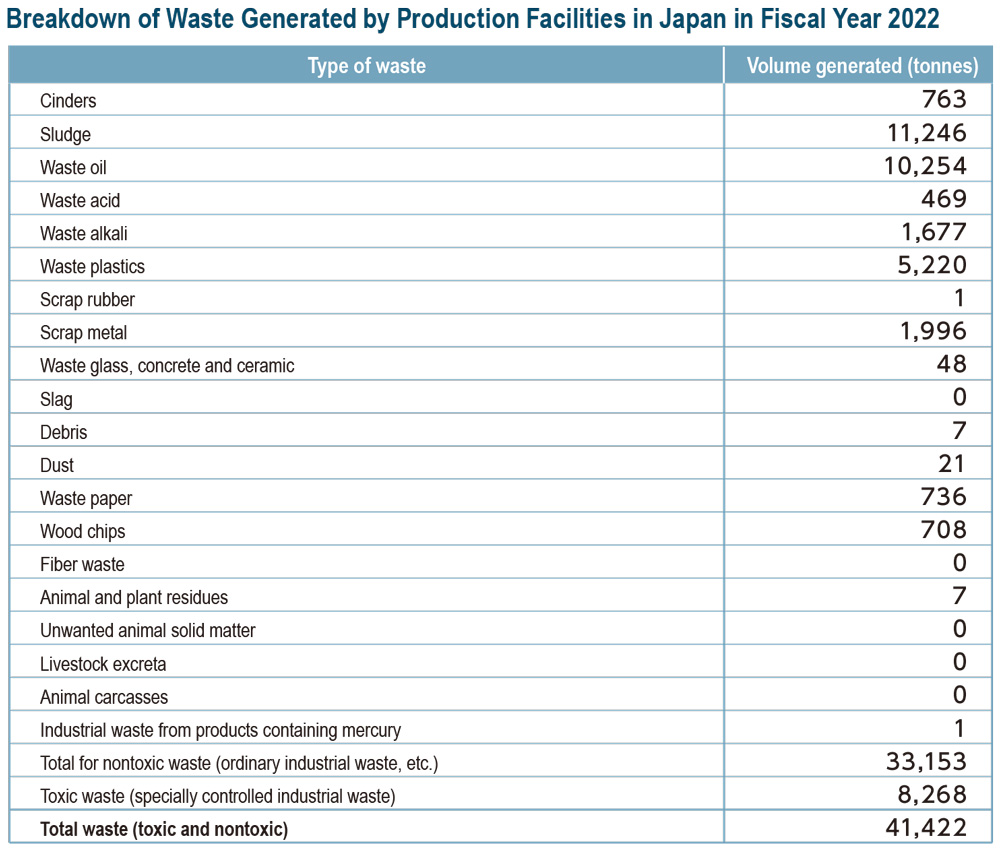
In fiscal year 2022, the DIC Group in Japan met its target for industrial waste generated by Group production facilities in Japan, which amounted to 41,422 tonnes, a decrease of 3% from fiscal year 2021, thanks to robust initiatives at individual facilities. The Group also outpaced its target for industrial waste disposed of as landfill by Group companies in Japan, which totaled 173 tonnes, down 13% from the previous period, as a result of which it also achieved a decline in industrial waste disposed of as landfill. Going forward, the Group will continue to reinforce its zero emissions initiatives. Group companies also pressed ahead with efforts to ensure the appropriate disposal of equipment containing PCBs and of unprocessed waste. The disposal of unprocessed waste was completed in the first half of fiscal year 2023.
02Initiatives Related to Waste Plastics
The Act on Promotion of Resource Circulation for Plastics, which came into force in April 2022, obliges companies to make efforts to recycle plastic resources throughout a product’s life cycle, from design through to final disposal. Companies responsible for generating waste plastics specified by the Act are taking steps to curtail the volume they generate and to expand recycling into new plastic resources. As both DIC and DIC Graphics each generate more than 250 tonnes of waste plastics annually in Japan, it is expected that they will be considered by the Act as businesses with high-level emissions. The two companies are currently collecting pertinent data for fiscal year 2022 and will disclose this information in the DIC Report beginning in fiscal year 2023. Other domestic Group companies will also disclose fiscal year 2022 emissions data. Looking ahead, the Group will continue striving to reduce its generation and increase its recycling of waste plastics.
VOICE
GENESYS ECO has helped to both save labor and ensure legal compliance.

Owing to the partial revision of Japan’s Waste Management and Public Cleansing Law, Japanese companies with sites that discharge 50 tonnes or more of what is classified as “specially controlled industrial waste” are obliged to introduce the e-Manifest system by April 2020. DIC took swift steps to comply with this requirement, achieving full-scale introduction in fiscal year 2017. The following year, we expanded deployment to include Group companies and systematized manifest notification, thereby lowering the risk of legal violations. Further, simplifying procedures for issuing manifests and automating annual reporting to authorities has helped us to both save labor and ensure compliance. However, because the timing of deployment has varied, the capabilities of pertinent personnel vary from one site to another. Accordingly, we will take steps to further standardize procedures and correct disparities in skill levels.
Manager, Safety and Environment Group, Sakai Plant, DIC Corporation
Eiji Ishii
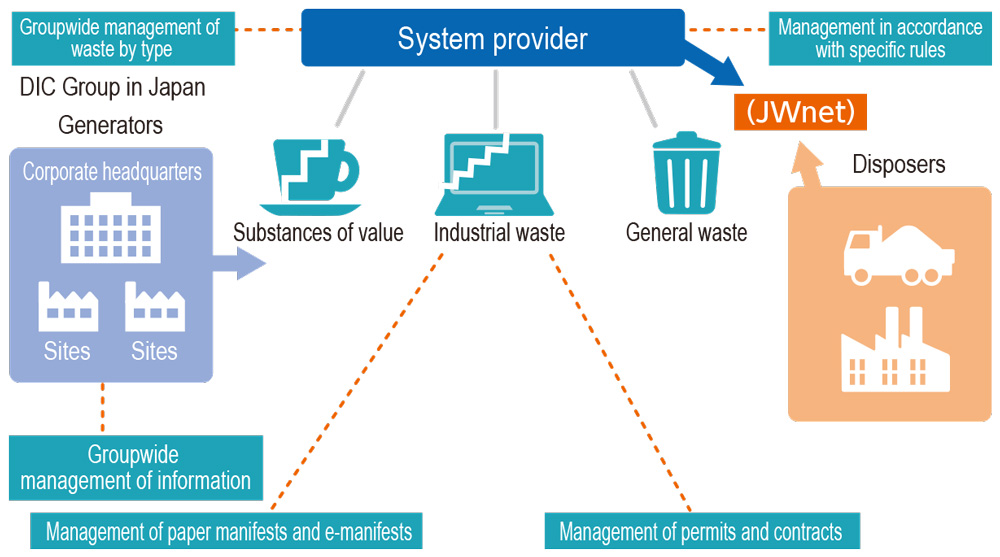
03Deployment of a Comprehensive Industrial Waste Management System
Japan’s e-Manifest system helps manage the movement of industrial waste by facilitating the electronic transmission of manifest information and tracking the flow of waste from generation through transport, intermediate treatment and disposal. In fiscal year 2016, the DIC Group in Japan introduced GENESYS ECO, a comprehensive industrial waste management system, for use with the e-Manifest system. Deployment of this system was completed at all Group production sites in fiscal year 2019, an achievement that has helped to both save labor and ensure legal compliance.
TOPICS
DIC Graphics (Thailand)’s Amata Plant Receives Gold Level in AFS’ 2021 Best Waste Management Awards
On January 31, 2022, DIC Graphics (Thailand) Co., Ltd.’s Amata Plant received a Gold Level award in the 2021 Best Waste Management Awards, which are presented by Amata Facility Services Company (AFS), Thailand’s largest industrial estate development and management company.
The Best Waste Management Awards are given to companies with operations at its Amata City industrial estates that exhibit excellence in the reduction of waste disposed of as landfill and handling of other waste, in line with the “3Rs” of waste management, namely, reduce, reuse and recycle. Through this awards program, AFS aims to raise awareness of the importance of effectively managing industrial waste across all of its estates. “DIC Graphics (Thailand)’s Amata Plant first participated in this program in 2019,” explains the company’s Chief Operating Officer Chaiyasit Adchariyaporn. “In 2020, we were unable to take part as responding to COVID-19 took precedence. In the year ahead, we will further strengthen waste management efforts with the aim of achieving zero disposal of waste as landfill and earning a Platinum Level award in 2022.”
In 2021, 78 participating production facilities were assessed and recognized in the Best Waste Management Awards program’s Silver, Gold and Platinum Level categories.

Kanitta Mahasamut, ESH supervisor (left) and Siwapol Yangthong, factory manager (center), of DIC Graphics (Thailand)’s Amata Plant

04DIC Group in Other Countries and Territories
In addition to ensuring that disposal of industrial waste complies with national and regional legal and regulatory requirements, the DIC Group’s production facilities outside Japan work to minimize waste through the voluntary recycling and reuse of materials. At production facilities in the Americas and Europe, Greater China and the Asia–Pacific region, the Group is introducing new waste treatment systems and promoting the horizontal deployment of best practices, including those aimed at improving production processes. In fiscal year 2022, waste generated by DIC production sites in other countries and territories totaled 76,851 tonnes, up 20% from fiscal year 2021. This significant increase reflected the inclusion for the first time of data for the Colors & Effects pigments business in results for the Americas and Europe. Waste disposed of as landfill be these sites rose 16%, to 17,041 tonnes. Going forward, the Group’s regional headquarters outside Japan will focus on reinforcing compliance with local laws and regulations, as well as curbing the generation of industrial waste and the disposal thereof as landfill.
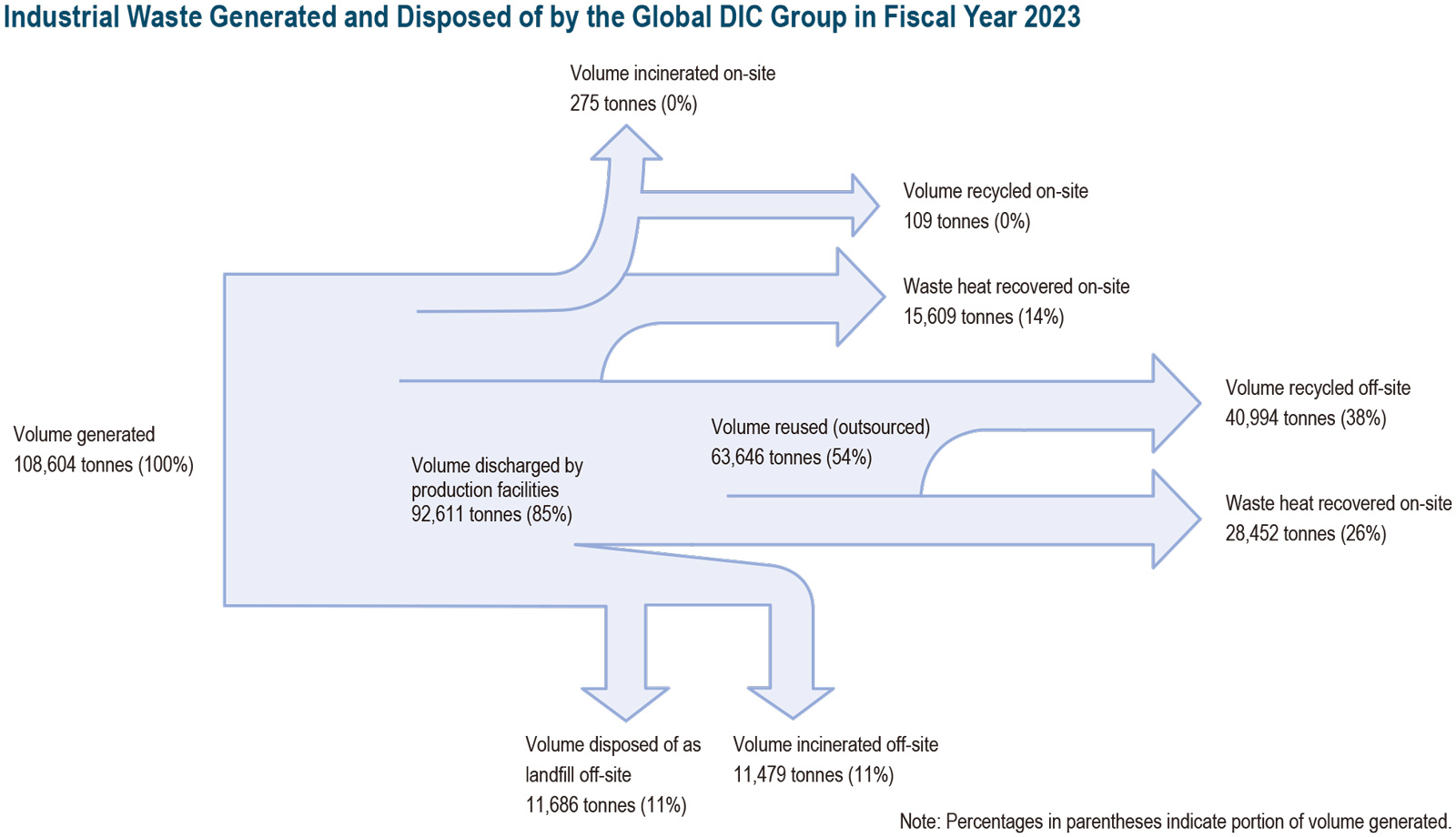
05Generation and Disposal of Industrial Waste by the Global DIC Group
The definition of “industrial waste”—including whether it encompasses both toxic and nontoxic substances, and both hazardous and nonhazardous substances—varies in different countries and regions, as do the methods used to dispose of such waste. The DIC Group works to ensure the management of industrial waste in a manner appropriate for the degree of danger posed and in compliance with the laws of the countries and territories in which its sites are located. The Group works to fully grasp and manage industrial waste on a global basis, from generation at production facility through to discharge, intermediate treatment and final disposal as landfill. The chart below illustrates the generation and disposal of industrial waste by the global DIC Group in fiscal year 2022. As this shows, the Group breaks down and calculates amounts at all stages of the industrial waste disposal process.