Preventing Environmental Pollution
Goals and Achievements of Major Initiatives
Reduce emissions of VOCs into the air.
| Scope of target | Fiscal year | Goals | Achievements | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | 2024 | DIC Group in Japan: 280 tonnes (Maintain at 50% decrease from fiscal year 2000) |
DIC Group in Japan: 176 tonnes | ★★★ |
| 2025 | DIC Group in Japan: 280 tonnes (Maintain at 50% decrease from fiscal year 2000) |
― | ― |
- Evaluations are based on self-evaluations of current progress.
Key: ★★★ = Excellent; ★★ = Satisfactory; ★ = Still needs work
Basic Approach
The DIC Group works to grasp the environmental impact of its operating activities and promotes systematic measures to reduce its environmental footprint. The Group also advances efforts aimed at preventing environmental pollution.
The DIC Group operates globally and handles chemical substances across multiple regions. The Group must therefore comply with pertinent environmental laws and regulations in different countries and territories, as well as advance initiatives to prevent environmental pollution. Specifically, the Group works continuously to reduce harmful emissions into the air and the discharge of pollutants into public bodies of water. For example, in addition to lowering emissions of hazardous substances (NOx, SOx and dust) and chemical oxygen demand (COD), the Group works to reduce emissions of substances targeted under various pollutant release and transfer register (PRTR) schemes and of volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Principal Initiatives in Fiscal Year 2024
01Reducing emissions of VOCs
In Japan, the DIC Group has worked since fiscal year 2005 to reduce emissions into the air, water and soil targeted under the Act on Confirmation, etc. of Release Amounts of Specific Chemical Substances in the Environment and Promotion of Improvements in the Management Thereof (substances targeted by Japan’s PRTR) and of substances targeted for management under a voluntary scheme created by the Japan Chemical Industry Association (JCIA).*1
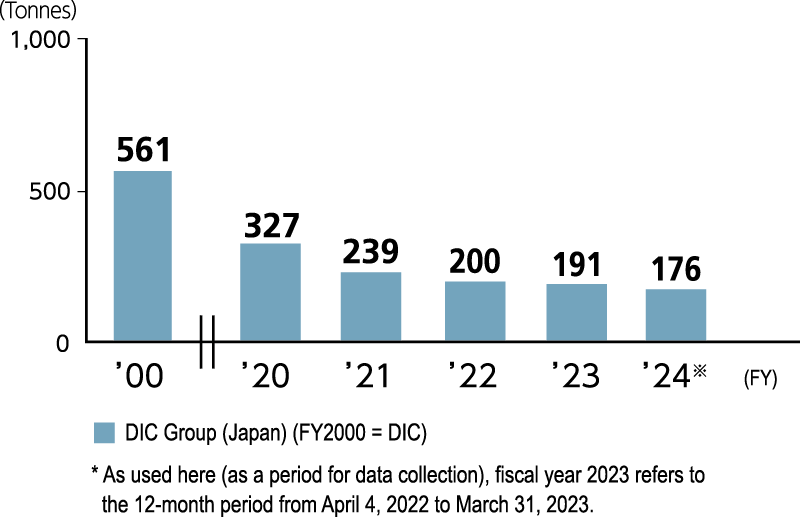
The DIC Group in Japan succeeded in achieving its voluntary target for reducing emissions of VOCs into the air for fiscal year 2010—30% from the fiscal year 2000 level—in fiscal year 2007. The Group has since raised this target to a 50% decrease from the fiscal year 2000 level, and has set a goal of maintaining its emissions of VOCs at this level. In fiscal year 2024, DIC Group companies in Japan reported total emissions of VOCs of 176 tonnes, a decline of 8% from fiscal year 2023. DIC Group companies in the People’s Republic of China (PRC) and the Asia–Pacific region also continue to conduct careful monitoring of VOC emissions. In the PRC, in particular, the Group is updating equipment and stepping up emissions management practices in response to the tightening of pertinent local regulations. The Group previously collected data for the 12-month period from January through December, but effective from fiscal year 2023 this has been changed to April through March of the following year, consistent with the reporting period specified in the aforementioned law.
- The JCIA is a general incorporated association. As one of Japan’s major industry organizations, the JCIA is a member of the ICCA and pursues the healthy development of the chemicals industry together with other chemical–industrial organizations around the world.
- A PRTR is a scheme for assessing, aggregating and disseminating data on the source of hazardous chemicals, amounts released into the environment and amounts transferred off-site from industrial establishments via waste products.
- The “551 substances and one substance group” comprises 462 class 1 chemical substances designated by the PRTR and 89 PRTR-designated substances (other than class 1) and one substance group (chain hydrocarbons with up to 4–8 carbon atoms) targeted for study by the JCIA.
The DIC Group in Japan monitored 462 class 1 chemical substances designated by the PRTR and 89 PRTR-designated substances (other than class 1) and one substance group (chain hydrocarbons with up to 4–8 carbon atoms) in fiscal year 2023. During the period, Group companies in Japan used and/or produced a combined total of 115 of these substances in amounts exceeding 1.0 tonne.
Environmental Emissions of VOCs (551 Targeted Substances, Including Those Designated by Japan’s PRTR, and One Substance Group) in Japan in Fiscal Year 2024
| DIC Group (Japan) | |
|---|---|
| Emissions into the air | 176 tonnes |
| Emissions into water | 3 tonnes |
| Emissions into soil | 0 tonnes |
| Total | 179 tonnes |
Targeted Chemical Substances for Which Emissions Exceeded 10 Tonnes in Fiscal Year 2024
| Substance | DIC Group (Japan) |
|---|---|
| Emissions into the environment | |
| Ethyl acetate | 80 tonnes |
| Toluene | 25 tonnes |
| Methyl ethyl ketone | 16 tonnes |
02Reducing SOx, NOx and COD
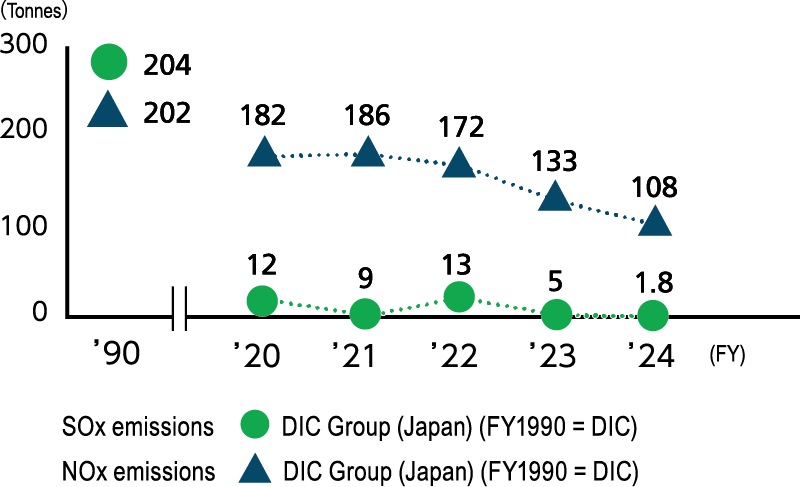
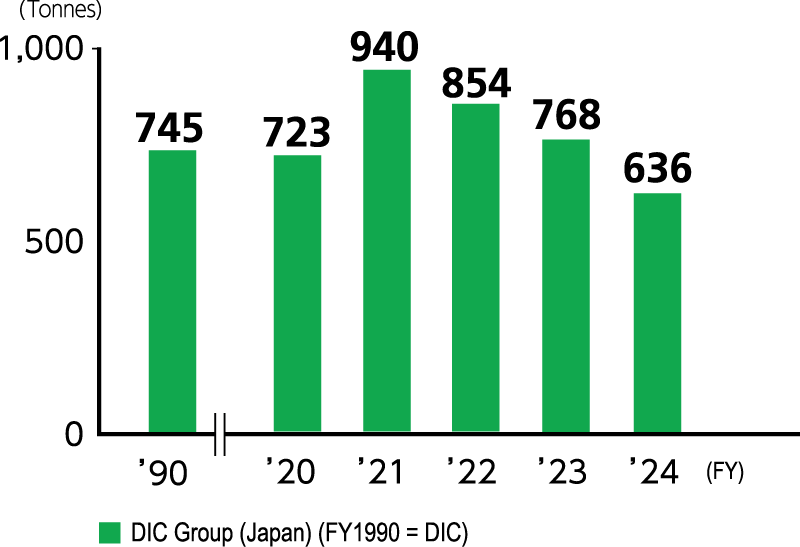
Taking fiscal year 1990 as the base year, the DIC Group in Japan has taken steps to reduce SOx and NOx emissions from boilers. The Group has also worked to reduce COD, an indicator of environmental impact in wastewater. Specific measures include installing biomass boilers and modifying production processes. In fiscal year 2024, emissions of SOx by the Group in Japan amounted to 1.8 tonnes, a decline of more than 99% from the fiscal year 1990 level, while emissions of NOx were 108 tonnes, a decrease of 45% from fiscal year 1990. The domestic DIC Group’s COD was 636 tonnes, down 21% from fiscal year 1990 and 23% from fiscal year 2023, with principal contributing factors including a change in the scope of consolidation. The Group will continue working to reduce COD by promoting the effective management of water quality.
DIC Group companies in other countries and territories are also switching from diesel to natural gas, and from diesel- and heavy oil–fired boilers to biomass boilers. To reduce COD, these companies are promoting the reuse of water and the installment of environment-friendly closed-loop recycling and wastewater treatment systems that purify wastewater to a level that exceeds that mandated by local laws.
03Complying with Regulations Governing Emissions of Dioxins
In Japan, the DIC Group monitors emissions of dioxins from facilities that produce these byproducts, in accordance with the Act on Special Measures Against Dioxins. At present, the Group has five such facilities in Japan, each of which has achieved reductions that surpass the standards set forth in the Act.
Dioxin Concentrations in Waste Gas and Wastewater Emissions for DIC Group Incinerators in Japan in Fiscal Year 2024
| Site | Waste gas | Wastewater | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (ng-TEQ/m³) |
Emissions reported in fiscal year 2023 (ng-TEQ/m³) |
Emissions reported in fiscal year 2024 (ng-TEQ/m³) |
Standard (pg-TEQ/ℓ) |
Emissions reported in fiscal year 2023 (pg-TEQ/ℓ) |
Emissions reported in fiscal year 2024 (pg-TEQ/ℓ) |
|
| Chiba Plant (DIC) |
5 | 0.19 | 0.74 | 10 | 0.036 | 0.021 |
| 10 | 2.7 | 3.5 | ||||
| Hokuriku Plant (DIC) |
5 | 0 | 0.00000093 | 10 | 0.0027 | 0.00038 |
| Sakai Plant (DIC) |
5 | 0.00000051 | 0.0000024 | NA | – | – |
| Sakai Plant (DIC Material Inc.) |
5 | 0.00000063 | 0.00000042 | NA | – | – |
| Hokkaido Plant (DIC Kitanihon Polymer Co., Ltd.) |
10 | – | – | NA | – | – |
| Tohoku Plant (DIC Kitanihon Polymer Co., Ltd.) |
10 | 0.0031 | 0.014 | NA | – | – |
04Ensuring the Appropriate Collection and Storage of PCBs
DIC Group companies in Japan work to ensure the appropriate collection, storage and management of equipment containing polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), including older-model transformers and capacitors, in accordance with the Law Concerning Special Measures for Promotion of Proper Treatment of PCB Wastes. These companies also ensure that equipment containing PCBs is disposed of in accordance with the practices of Japan Environmental Storage & Safety Corporation (JESCO). The DIC Group in Japan completed disposal of waste with high concentrations of PCBs in fiscal year 2023. Efforts to manage and dispose of low-concentration PCB waste are proceeding apace.
05Responding to Asbestos Risks
The DIC Group in Japan strives to respond to potential risks associated with asbestos during demolition or when retrofitting equipment, as outlined in the Ordinance on the Prevention of Health Impairment due to Asbestos and the revised Air Pollution Control Law.
06Soil and Groundwater Pollution
In addition to complying strictly with the Soil Contamination Countermeasures Act, the DIC Group in Japan implements soil and groundwater surveys and countermeasures as necessary to assess related risks. In fiscal year 2021, a voluntary survey conducted at a site belonging to the Hokuriku Plant revealed soil contamination and resulted in the site being designated as an “area which requires measures.” Purification measures are being implemented in line with the Act. In fiscal year 2024, a soil contamination investigation was conducted at the site of the Chiba Plant as required by the Act following any change in the land characteristics of any area beyond a certain size. Soil contamination was discovered, leading to the site’s designation as an “area for which changes to form or nature require notification (controlled area for landfill).” Accordingly, the Group intends to carry out contamination removal.