Special Feature Hybranch® : Hyperbranched Polystyrene
Enhancing the environmental performance of food containers, electrical appliance components and insulating materials
Social Imperative Provide superior resin that help reduce use of resources and energy in and increase the recyclability of food containers
Polystyrene and clear plastic containers that keep food products fresh are essential to food sanitation, preventing contamination during transportation and storage and the deterioration of quality due to changes in temperature and humidity. Plastic containers are also light and strong and thus consume little energy during transportation. In Japan, the materials used in such containers can be recycled and reused in various products in line with the Containers and Packaging Recycling Act.
Nonetheless, the plastics are made with petroleum and a considerable amount of energy is used in their production. Moreover, plastic containers account for a significant volume of household container and packaging waste. From the perspective of helping to prevent global warming and resource depletion, the development and promotion of more resource-efficient materials is a crucial challenge.
DIC’s Response Develop revolutionary thin polystyrene that resists tears and breaks
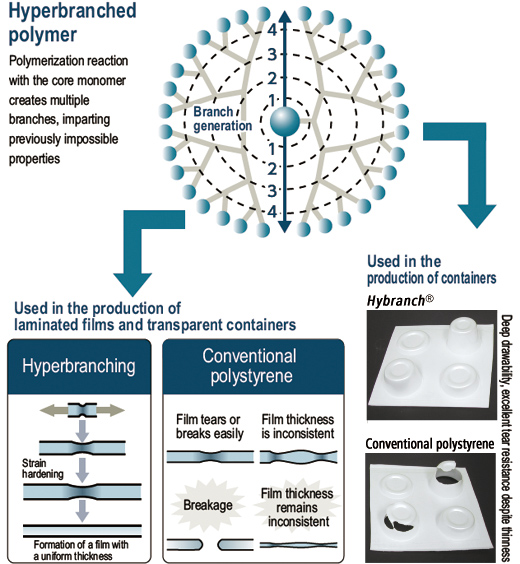
Thanks to its extensive R&D in the area of polymerization, DIC succeeded in developing a revolutionary repetitively branched molecule (dendrimer), for which it also became the first in the world to develop a mass production technique, called hyperbranching. This technique takes performance to new heights by creating multiple branches, or small molecules, through a polymerization reaction with the core monomer.
DIC has used this technique in the production of polystyrene—a popular material for containers and packaging—achieving a material that is lighter and thinner, yet more resistant to breaks, than conventional polystyrene, and has greater tear resistance than conventional laminated films. DIC’s Hybranch® polystyrene thus facilitates the production of containers and films that are thinner and lighter than those made with conventional polystyrene. Molding to a more precise thickness and at a low temperature also ensures higher productivity and reduces energy used in production. Other benefits include high recyclability and quality even after recycling.
In addition to supplying major manufacturers of food containers, DIC markets Hybranch® to manufacturers of, among others, high-polymer refrigerator trays. Other applications that leverage the outstanding performance of Hybranch® include housing insulation.
Conventional polystyrene is produced using a process that involves feeding a liquid monomer and an initiator into a reactor, mixing to cause a polymerization reaction and removing heat generated as a result thereof. In contrast, at DIC plants this process is centralized in a single cylindrical static mixer reactor that mixes the raw materials as they pass through multiple tubes and simultaneously removes heat generated as a result of the polymerization reaction. This eliminates the need for mixers, facilitates the simplification of cooling units and reduces energy use.
In response to expanding demand for Hybranch®, DIC revamped the general-purpose polystyrene production facilities at its Yokkaichi Plant. As a result, in April 2014 the Company increased its production capacity for hyperbranched polystyrene by 20%.
KEY PERSON of DIC
The establishment of an industrial technology—rather than a theory limited to the laboratory—is a deeply significant achievement.

It is generally accepted that the flowability of a polymer necessarily decreases as its molecular weight increases. DIC’s proprietary polymer design, mixing and polymerization technologies enabled us to overturn this notion. I believe it is very significant that DIC was the first in the world to establish an industrial technology that facilitates stable mass production of a hyperbranched polystyrene, rather than simply a theory the application of which is limited to the laboratory. This was possible thanks to an environment that encourages close collaboration between basic and developmental research groups. Going forward, we intend to further strengthen the framework for in-house collaboration in development efforts.
The fact that we intend to capitalize on our hyperbranching technique in the production of not only specialized products but also general-purpose polystyrene, which is used in a broad variety of markets, is also important. Looking ahead, we will collaborate with marketing teams to explore the potential for applying this technique in the development of plastics for use in other fields.
Head Researcher, Polymer Technical Group 3, Polymer Technical Div.1 Tsuyoshi Fukukita
Our goal is to establish Hybranch® as the domestic standard and then to turn our attention to growing Asian markets.

Hybranch® initially earned praise for its outstanding film-forming capability. Applications were later expanded to included foamed polystyrene and refrigerator trays. Customers who used the product in the production of molded items gave Hybranch® top marks for improving productivity, as well as for facilitating the production of lighter products, thereby providing cost benefits when recycled in line with the Containers and Packaging Recycling Act.
Looking ahead, our goal is to establish Hybranch® as the unassailable domestic standard. We will then turn our attention to the increasing number of Japan-based supermarkets, convenience stores and electronics manufacturers setting up operations in growing Asian markets. We are confident that building a strong brand presence for Hybranch® in these markets will not only help customers improve productivity but also contribute to the reduction of resource and energy use, thereby reducing the negative impact of these companies’ operations on the environment.
Polystyrene Marketing Dept., Packaging Materials Sales Div. Takashi Kanno
Special Topics 2014

Ceranate® : Hybrid Resin for Coatings
Seeking to shield houses and other structures from UV rays and air pollution

Hybranch® : Hyperbranched Polystyrene
Enhancing the environmental performance of food containers, electrical appliance components and insulating materials

Solar Cells : Materials for Solar Cells
Seeking to extend the lives of solar cell modules

Lithium Ion Batteries : Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Contributing to the evolution of high-performance batteries is essential in a smart technology-based society

Printed Electronics : Materials for Printed Electronics
Making today’s advanced information society easier to navigate and more environment-friendly
TOPICS
Sun Chemical Revamps its Website
The Sun Chemical Group, a core member of the DIC Group with operations in North America and Europe, recently revamped its website, improving search capability and simplifying navigation.
DIC Expands Supply Capabilities for Linablue® Natural Blue Food Coloring
Rising concern for the health benefits and safety of food is accelerating a shift toward using natural, rather than synthetic, colorings in the food products industry. As the world’s largest manufacturer of one of the few natural blue colorants in existence, the DIC Group intends to bolster its supply capabilities by building a new plant in the United States.