Management System
Basic Approach
The DIC Group promotes a broad range of ESH initiatives through its Responsible Care program.
Initiatives to Date
As a global organization that manufactures and sells chemical substances, the DIC Group promotes a broad range of ESH initiatives through its Responsible Care program. Having established its Principle and Policy for the Environment, Safety and Health in 1992, in 1995 DIC pledged to implement the precepts of Responsible Care. Since reaffirming its support for Responsible Care management in January 2006 by signing the CEO’s Declaration of Support for the Responsible Care Global Charter, the Company has promoted constant improvements. Today, the Group manages its Responsible Care program in a uniform manner using standardized codes, guided by its Environment, Safety and Health Policy, and works to implement initiatives that exceed regulatory requirements, in line with annual Responsible Care activity plans, and to fully disclose the results thereof.
Note:Responsible Care describes voluntary management initiatives undertaken by companies that manufacture or otherwise handle chemical substances, in line with the principles of autonomous action and self-assessment, pledging in their management policies to protecting the environment and ensuring health and safety across the entire life cycle of products, from development to manufacturing, distribution, use and end-of-life disposal, as well as to disclosing related information and promoting improvements.

Responsible Care Codes
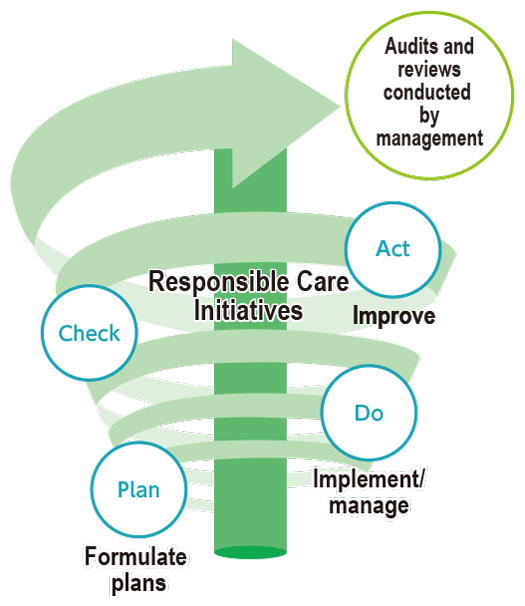
The DIC Group manages its Responsible Care program in accordance with seven codes:* “Occupational safety and health” (protection of the safety and health of employees), “disaster prevention” (prevention of fires, explosions and the discharge of chemicals), “environmental protection” (continuous reduction of chemical emissions and the discharge of waste), “safety in logistics” (reduction of chemical risks associated with the distribution of chemicals), “chemical substance safety” (management of risks associated with chemicals), “dialogue with society” (communication with local communities regarding ESH) and “management systems” (ensure the uniform administration of the first six codes). In line with these codes, the Group applies the PDCA cycle and conducts annual ESH audits and management reviews to evaluate initiatives.
- The seven Responsible Care codes were developed by the Japan Responsible Care Council (JRCC), which is part of the JCIA, as a framework for Responsible Care programs with the goal of helping achieve a society that supports efforts to address ESH-related initiatives.
- Occupational safety and health (protection of the safety and health of employees)
- Disaster prevention (prevention of fires, explosions and the discharge of chemicals)
- Environmental protection (continuous reduction of chemical emissions and the discharge of waste)
- Safety in logistics (reduction of chemical risks associated with the distribution of chemicals)
- Ensuring the safety of chemical substances safety (management of risks associated with chemicals)
- Engaging with society (communication with local communities regarding ESH)
- Management systems (ensure the uniform administration of the first six codes)
Message from the President
DIC’s president prepares a message for employees for Environment Month and National Safety Week.
Responsible Care Education
As a company that manufactures and sells chemical substances, DIC incorporates education regarding the importance of Groupwide Responsible Care efforts into training for new employees (both new graduates and mid-career hires). Ongoing education is provided as part of rank-specific training for newly promoted employees.

Framework for Promoting Responsible Care
The Sustainability Committee, which answers directly to the president and CEO, is responsible for setting Responsible Care initiatives. Currently chaired by the president and CEO, the committee includes business group presidents, administrative unit heads, CEOs of regional headquarters and members of the Audit & Supervisory Board. The committee formulates Groupwide sustainability targets and policies, as well as deliberates and evaluates medium-term sustainability policies and annual sustainability initiatives. The PDCA cycle is used to evaluate voluntary Responsible Care initiatives implemented by Group companies, plants and R&D facilities in collaboration with the Safety and Environment Group. The Responsible Care Department provides support to ensure the smooth progress of these initiatives and conducts audits to ensure compliance and improve safety and environmental performance.
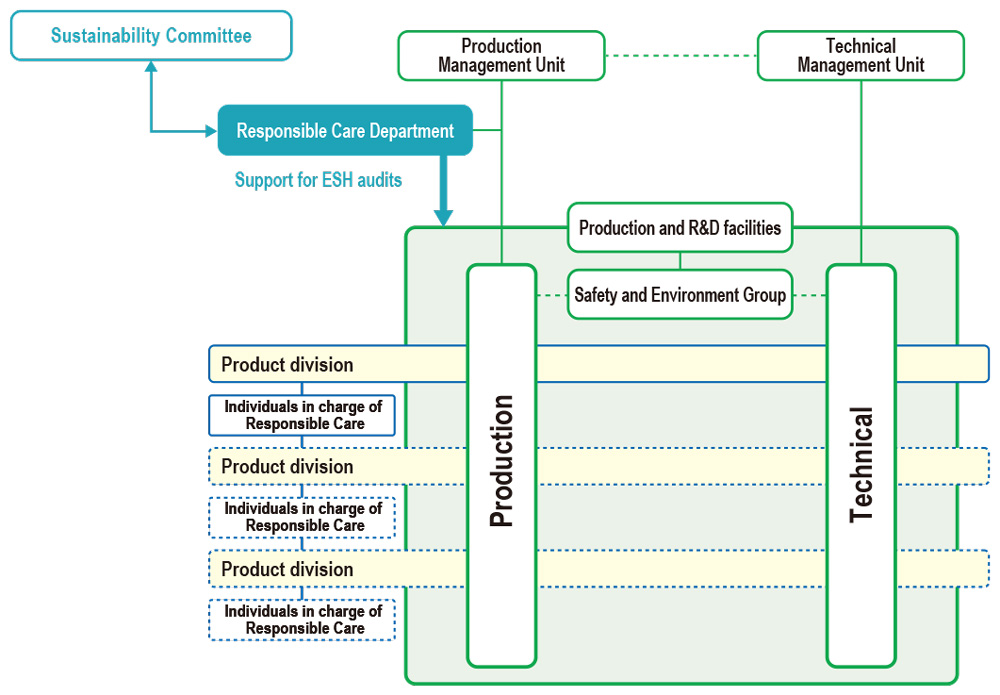
Deployment of Responsible Care Initiatives at Group Companies
The Responsible Care Department provides wide-ranging support to DIC Group companies worldwide, regardless of operating scale, with the goal of enhancing Responsible Care initiatives Groupwide. Of particular note, the department assigns representatives to assist regional headquarters overseeing Group operations in Greater China and the Asia–Pacific region, as well as supports local initiatives to foster human resources.
1. Initiatives in Japan
The DIC Group has 12 companies and 36 sites in Japan. Safety and Environment groups have been established at each site, which are overseen by the Responsible Care Department. DIC and DIC Graphics hold GM conferences, which are gatherings of ESH officers from principal sites who have been appointed group managers, four times a year. Other domestic Group companies participate in twiceannual Responsible Care conferences. These various conferences facilitate the discussion of efforts to prevent accidents and disasters, share information on environmental challenges and ensure common awareness of Groupwide rules.
TOPIC
DIC and DIC Graphics Establish Horizontal ESH Framework
During a meeting with management in fiscal year 2021, ESH officers proposed that steps be taken to strengthen communication among DIC Group sites in Japan. This led to the establishment of a horizontal framework linking of ESH officers from all 36 of these sites.
Before this, information sharing among site ESH officers frequently tended to deteriorate whenever anyone retired or was reassigned. Since fiscal year 2020, we have seen opportunities for communication among sites decline even further as a result of COVID-19. New people, in particular, have been unable to network. With the aim of improving this situation, we set up a horizontal framework to encourage cross-site interaction, primarily through online activities. This began with the idea that a horizontal line through the Group’s vertical corporate organization would make it easier to share information with each other and bolster site ESH initiatives. To encourage communication, we have introduced online chats for sharing concerns regarding such initiatives and regular online meetings to facilitate face-to-face exchanges. In addition to continuing with current activities, we look forward to creating chances for site ESH officers to meet in person.

Manager, Safety and Environment Group,
Komaki Plant
Kazuhito Ishida

Safety and Environment Group,
Gunma Plant
Hiroshi Noguchi
We have introduced an information management system to enhance our Responsible Care program.

Global companies today disclose a variety of sustainability-related information, including on the environment and energy. Previously, the Responsible Care Department would receive necessary data by email from site environmental officers, which it would then aggregate and release. However, because DIC has regional headquarters in the PRC and the Asia–Pacific region, as well as its corporate headquarters in Japan, and more than 70 sites worldwide, the volume of data was massive and management was complicated. For this reason, we introduced a cloud-based service from a Japanese IT vendor and adopted a method whereby Responsible Care officers at each site input data into a common database, making it easily accessible to the Responsible Care Department, as well as by regional headquarters. This centralized data management and streamlined aggregation. In introducing this system, we took care to carefully explain objectives to Responsible Care officers at each site and prepared an illustrated user manual in Japanese, Chinese and English so as to minimize the burden on individual officers. We also developed a new program and standards for data collection, making it possible to amass more detailed data than in the past. Currently, the system is used to collect data in line with eight individual themes in the three categories of “environment,” “energy” and “occupational safety and health.” We intend to increase the number of themes with the aim of helping to further enhance the effectiveness of our Responsible Care program.
Assistant Manager, Safety and Environment Group, Responsible Care Department, DIC Corporation Masayuki Iwakubo
2. Initiatives in the Asia–Pacific Region
The DIC Group has 17 companies and 23 sites across the Asia–Pacific region. DIC has installed ESH country heads (individuals in charge of ESH initiatives) in 10 countries and territories in the region under the supervision of a regional ESH director, who has been installed at DIC Asia Pacific, the Group’s regional headquarters, in Singapore. An annual conference and regular quarterly meetings involving the Responsible Care Department in Tokyo, the regional ESH director and the ESH country heads are held to ensure effective communication. The Responsible Care Department has also dispatched an ESH manager from corporate headquarters to provide on-site guidance. Country heads hold country- and territory-specific meetings periodically to consider initiatives, targets and challenges.
The fiscal year 2022 edition of the DIC Asia–Pacific Region Annual ESH Conference was held in November. Unlike in fiscal years 2020 and 2021, when the conference was held online due to COVID-19, ESH country heads, site ESH officers, the regional ESH manager, the director in charge of regional Group operations and Responsible Care Department staff gathered in person in Indonesia. Participants discussed ESH policies, targets and challenges for fiscal year 2023.
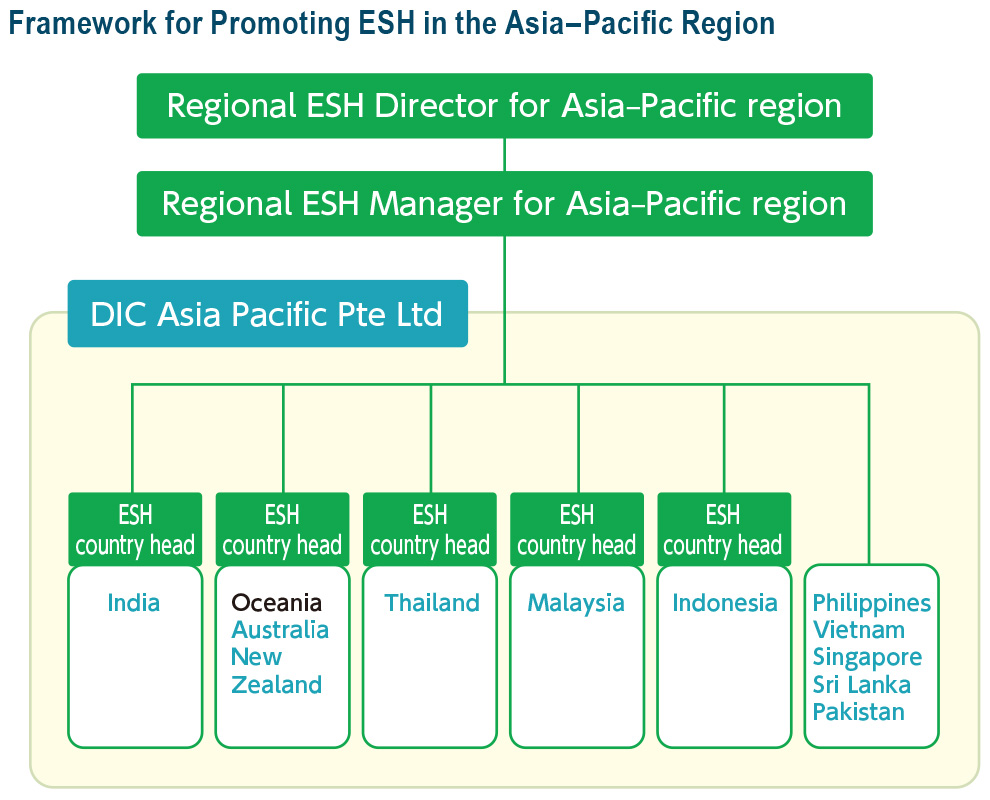
Framework for Promoting ESH in the Asia–Pacific Region
3. Initiatives in Greater China
In Greater China, the DIC Group has 16 companies and 17 sites. DIC has installed a regional ESH director at DIC (China), the Group’s regional headquarters, in Shanghai. The Company has also reinforced its regional ESH framework by assigning ESH coordinators to oversee efforts in the southern and eastern parts of the country. An annual conference and regular teleconferences involving the Responsible Care Department in Tokyo, the regional ESH manager and the ESH coordinators are held to ensure effective communication. The Responsible Care Department has also dispatched an ESH manager from corporate headquarters to provide on-site guidance.
The fiscal year 2022 Greater China Annual ESH and Energy Conservation Conference was held in November. As in the previous two fiscal years, the conference was held online because of COVID-19. Participants, which included site ESH officers, the regional ESH manager, the director in charge of regional Group operations and Responsible Care Department staff, discussed ESH policies, targets and challenges for fiscal year 2023.
4. Initiatives in the Americas, Europe and Africa
The Sun Chemical Group oversees all Responsible Care initiatives by DIC Group companies in the Americas, Europe and Africa. With the aim of ensuring the DIC Group’s ESH policy and its values are shared by all, the Responsible Care Department in Tokyo holds periodic online conferences and ESH manager meetings with local Responsible Care staff. The Responsible Care initiatives of the Colors & Effects pigments business, the acquisition of which was completed in July 2021, are also overseen by the Sun Chemical Group.
VOICE
Thoughts on Daily Efforts to Ensure Safety

What does “safety” mean? At my previous company, it was endless classes, protective gear to change into before starting work, frontline risks to comprehend, safety notices on the walls and written rules. At DIC, it is the education and training I attend, the protective gear I put on, the risks I identify, the safety notices that I am consistently aware of and the rules that I observe without fail. These may sound pretty much the same on the surface, but in fact the safety culture of the two companies is really very different.
From Companywide emergency drills to itemized emergency response plans, the monthly sharing of case studies and meticulous on-site work processes, DIC’s approach reflects the people-first philosophy that underscores its safety culture. All around us, there are protective guards on sharp-cornered control panels and fluorescent labels on stairs to prevent falls. Every day at our morning meeting, key passages from Principles of Safe Conduct are read aloud. An effective safety culture is a result of the daily accumulation of experience and know-how. In this environment, my mindset changed. I began to see safety not as something being forced on me, but rather something that I do of my own accord. This is the sentiment conveyed in DIC’s safety slogan, “Safety is one’s own responsibility.”
Qingdao DIC Finechemicals Co., Ltd. Yu Hezhi
TOPICS
DIC (China) Conducts Seminar to Improve DIC Group Safety Management Across Greater China
From November 10–12, 2021, DIC (China)’s ESH team conducted a seminar at DIC Synthetic Resins (Zhongshan) Co., Ltd., as part of an ongoing effort to build a culture of safety and improve leadership and skills in the area of safety management. The fiscal year 2021 seminar comprised courses under three headings: “Management and communication,” “environmental management” and “experiences implementing ESH management best practices.”
In the management and communication course, in particular, efforts focused on group discussions and role playing with the aim of ensuring the effectiveness of management processes. The environmental management course provided detailed explanations of arcane related laws and regulations to deepen understanding of strategies for and key aspects of environmental management over the life cycle of production equipment. The third course, which looked at ESH management best practices, centered on risk management, the securing of work permits, contractor administration and other day-to-day ESH activities, reaffirming the importance of leadership to safety management. Going forward, the DIC Group in Greater China pledges to continue working to improve safety management capabilities across the region.
DIC (China) Conducts Seminar to Improve Safety Management Across Greater China
In August 2020, DIC (China)’s ESH team conducted a seminar on advanced safety management principles and safety management tools at Qingdao DIC Finechemicals. Because of COVID-19, representatives from Hong Kong and Taiwan participated online. Local participants numbered 42 and included ESH officers and managers from the production and facility, equipment and ESH departments, underscoring increasing interest in safety management.
The seminar focused on the philosophy of advanced safety management, deciphering the elements of process safety management and mechanical integrity, as well as best practices of leading PRC-based chemicals companies and related safety management tools and methods. Lecturers included Shi Honglin, senior expert and deputy chief engineer at the China Chemical Safety Association; Li Zhuxing, a global partner of sustainability consultancy ERM, who had served as general manager of the risk management department of DNV GL in the PRC; a veteran manager from DuPont; and safety management training specialists from prominent local chemicals companies. DIC (China)’s ESH team will continue to monitor the level of safety management across the DIC Group in Greater China and plans to conduct seminars aimed at improving capabilities in this area on a periodic basis.
DIC (China) Conducts Training Program to Improve Safety Management Across Greater China
In June 2019, DIC (China)’s ESH team conducted a safety management improvement training program in Greater China. The program was attended by 26 individuals, including ESH officers and representatives of production and facility departments, from the PRC and Taiwan. The 2019 program began with the reading of a message prepared by DIC’s president and CEO for the PRC’s national safety week and focused on the two themes of ISO 45001 auditor training and ESH safety trainer instruction. ISO 45001 auditor training featured lectures on the history of ISO 45001, the International Organization for Standardization’s standard for occupational safety and health, in the PRC and an explanation of the standard by a researcher in the country’s occupational safety and health management framework and an individual involved in the standard’s creation. ESH safety trainer instruction, conducted by highly experienced coaches, emphasized training skills, the preparation of study materials and safety training–related R&D. The lectures were followed by an examination to earn ISO 45001 auditor qualification. All participants received passing marks. Looking ahead, these individuals will apply the basic expertise gained through this program to initiatives implemented at their respective workplaces. DIC (China)’s ESH team will monitor such initiatives with the goal of further enhancing safety management across the region.
Annual Activity Plans
The DIC Group formulates an annual Responsible Care Activity Plan and oversees Groupwide initiatives. Based on the Group’s annual plan, which is prepared by the Responsible Care Department, regional headquarters develop their own region-specific activity plans, while individual Group companies, in line with the concept of management by objectives (MBO), translate these plans into reality by promoting a variety of Responsible Care initiatives.
The DIC Group’s Annual Responsible Care Activity Plan for Fiscal Year 2022
-
Occupational safety and health
- The DIC Group’s fundamental objective remains the achievement of accident-free workplaces. With this in mind, set regional targets for total recordable incident rate (TRIR)*1 in fiscal year 2022 and implement related initiatives.
- Encourage safety and health awareness among all employees.
-
Disaster prevention
- Encourage the horizontal deployment of measures based on the lessons learned from past major accidents and take steps to prevent their recurrence.
- Conduct risk assessments with the aim of reducing process risks.
- With the aim of reducing process safety accidents, continue calculating such accidents in accordance with the International Council of Chemical Associations (ICCA) guidelines.
-
Environmental protection
- Maintain/lower the impact of production activities on air and wastewater quality.
- Reduce the generation of and maintain/increase the resource recycling rate*2 for industrial waste.
- Continue to assess water risks affecting production activities. Consider approaches to managing targets for the reduction of water consumption, among others.
- Implement initiatives aimed at improving environmental compliance.
-
Safety in Logistics
- Continue to provide information pertinent to the safe transport of chemicals.
-
Chemical substance safety
- Promote the creation of a new global system for managing chemical substance information.
- Further expand deployment of the Wercs and Atrion at DIC Group companies overseas.
- Increase understanding of domestic and overseas laws and regulations governing chemical substances and prevent violations thereof by further enhancing in-house legal and regulatory training, including at overseas Group companies.
-
Dialogue with society
- Continue to publicize the results of Responsible Care activities.
-
Management system
- Make use of the ESH data collection system.
- Reinforce relations between corporate headquarters and regional headquarters to prevent accidents/disasters in Greater China and the Asia–Pacific region.
- Rebuild environment- and safety-related management systems.
- Promote environment- and safety-related education.
- TRIR is calculated as (Number of casualties due to occupational accidents resulting in workdays lost + Number of casualties due to occupational accidents not resulting in workdays lost) / Million work hours
- Resource recycling rate is calculated as (Volume of industrial waste recycled (material recycling) + Waste heat recovered) / Volume of industrial waste generated